China is currently experiencing its largest recorded outbreak of the chikungunya virus, with more than 7,000 confirmed cases reported. The outbreak, which began in early July 2025, has hit the city of Foshan in Guangdong Province particularly hard, prompting local authorities to implement wide-reaching public health measures in an attempt to contain the disease.
Sudden Spike Alarms Health Officials
The number of chikungunya infections has risen dramatically over the past few weeks, taking both the public and medical community by surprise. Previously rare in China, the virus is believed to have been introduced through international travelers, and it quickly found a foothold in mosquito-friendly environments.
Chikungunya virus is spread through the bite of infected mosquitoes—primarily the Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus species. The illness is known for causing sudden high fever, intense joint pain, rash, fatigue, and headache. While not usually life-threatening, the virus can lead to serious discomfort and, in some cases, long-term joint issues, especially in older adults.
How Authorities Are Responding
Use of Drones and Fines
To identify and eliminate mosquito breeding grounds, drones are being deployed across cities in Guangdong Province. These aerial devices scan for areas with stagnant water—like rooftop containers, construction sites, and gardens—where mosquitoes can easily reproduce.
Also Read
Authorities have also enforced strict cleanup rules for residents and businesses. Those who fail to remove breeding sites from their property risk facing fines as high as 10,000 yuan (approximately USD 1,400). This strategy draws on methods used during past health emergencies, combining surveillance technology with community-level enforcement.
Biological Control Methods
In addition to human interventions, the local government is taking a natural approach to mosquito control. Officials have released fish that feed on mosquito larvae into water bodies and introduced so-called “elephant mosquitoes”—a harmless species that preys on mosquito larvae but does not spread diseases.
These biological methods aim to reduce mosquito populations without relying heavily on chemicals or pesticides.
Hospital Treatment and Monitoring
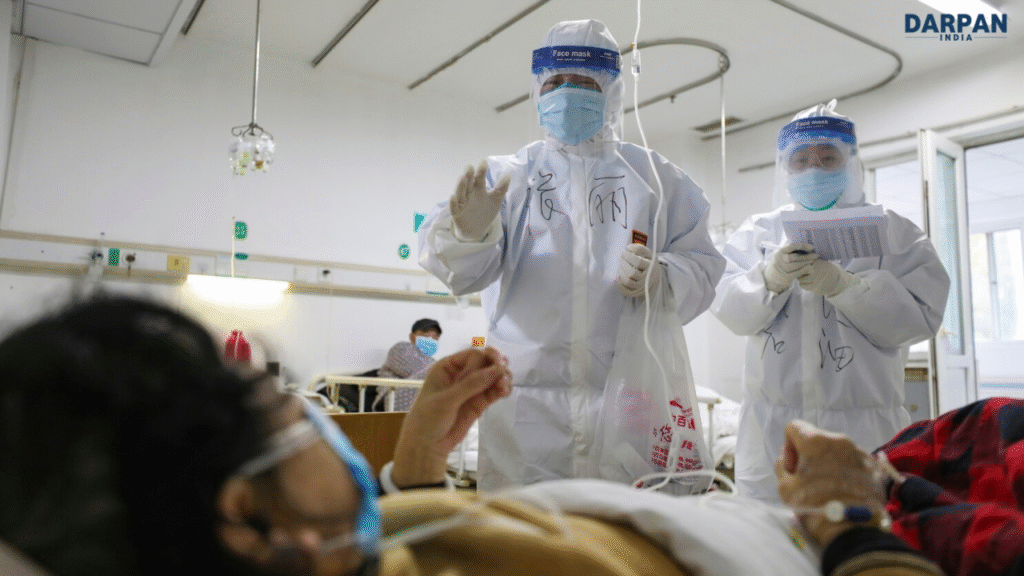
People who test positive for Chikungunya virus are being admitted to hospitals for observation and symptom management. Though home isolation is no longer mandatory, patients are encouraged to rest, hydrate, and take medication to reduce fever and inflammation.
Since Chikungunya virus cannot be spread from person to person, the focus remains on reducing mosquito populations and preventing bites during the infectious period.
Expert Opinions Raise Concern
Medical experts say this outbreak is unusual and concerning. Chikungunya virus had never spread so widely in China before, which means the population has little or no immunity. This makes it easier for the virus to spread quickly, especially in urban areas where mosquitoes thrive.
Health professionals are urging the public to stay alert, avoid mosquito exposure, and seek medical care promptly if symptoms appear. There are also calls for expanded testing, community education, and better environmental hygiene to stop the disease from reaching more densely populated areas.
Travel Alerts and Regional Impact
In response to the outbreak, international health agencies have issued travel advisories for southern China. Travelers are being asked to take additional precautions, including wearing long-sleeved clothing, using mosquito repellents, and staying in well-ventilated or air-conditioned spaces.
Airports and transportation hubs are also ramping up their awareness campaigns to inform passengers of the risks and symptoms. With rising global travel and climate conditions that favor mosquito breeding, similar outbreaks could soon appear in other parts of Asia or even farther afield.
Understanding Chikungunya
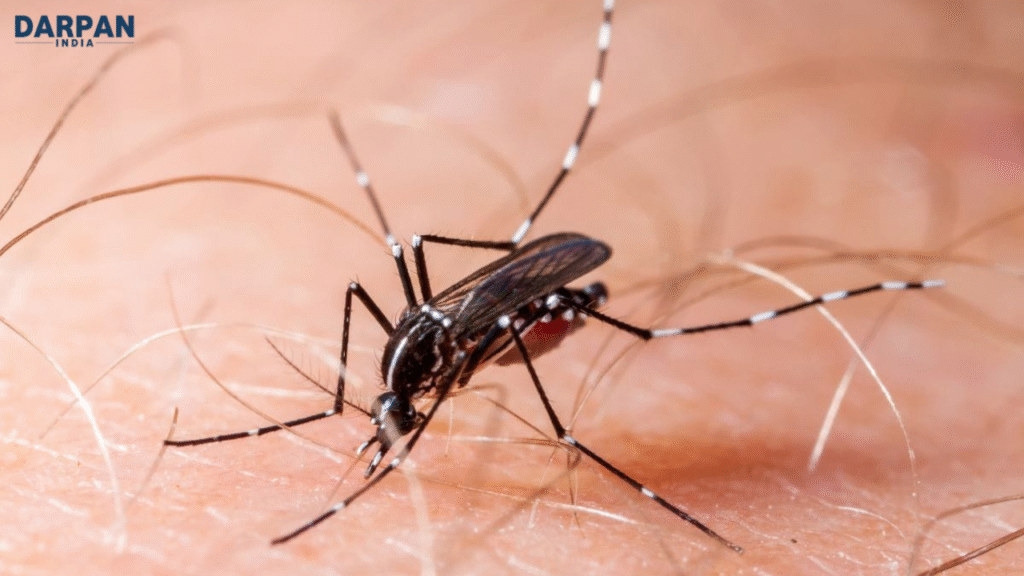

Chikungunya virus is a viral disease that typically shows symptoms within two weeks of infection. The most common complaint is severe joint pain, which can persist for weeks or even months. Although most people recover fully, some continue to feel the effects long after the virus has left their system.
Currently, there is no specific medicine to cure the virus. Doctors focus on relieving symptoms with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relief. In recent years, vaccines have been developed and approved in certain countries, but widespread access remains limited.
Why This Outbreak Matters
This outbreak is more than a local health issue—it serves as a reminder of how quickly vector-borne illnesses can emerge in unexpected places. As global temperatures rise and urban areas expand, mosquito habitats are growing, increasing the risk of diseases like Chikungunya virus appearing in regions where they were previously unknown.
The virus’s ability to spread rapidly, combined with a lack of prior exposure in the local population, has turned this outbreak into a major public health challenge. It also highlights the importance of preventive care, strong public health systems, and community cooperation.
China’s Path Forward
In the wake of this surge, Chinese authorities are increasing surveillance and continuing public education efforts. Communities are being urged to eliminate mosquito breeding grounds around homes and neighborhoods, including clearing gutters, covering water containers, and ensuring proper drainage.
Local health teams are also working on longer-term solutions, such as introducing environmental policies that limit mosquito breeding in construction zones and residential areas. Though the immediate focus is on controlling this outbreak, the lessons learned will likely shape China’s response to future health crises involving mosquito-borne illnesses.
चिकनगुनिया वायरस के चीन में 7,000 मामले सामने आए
चीन इस समय अपने इतिहास की सबसे बड़ी चिकनगुनिया वायरस की बीमारी से जूझ रहा है। जुलाई 2025 की शुरुआत से अब तक 7,000 से अधिक मामलों की पुष्टि हो चुकी है, जिनमें सबसे अधिक प्रभावित क्षेत्र गुआंगडोंग प्रांत का फोशान शहर है। इस अचानक फैले प्रकोप ने स्वास्थ्य अधिकारियों को तेजी से कार्यवाही करने पर मजबूर कर दिया है, जिसमें तकनीकी उपाय, जुर्माने और व्यापक सफाई अभियान शामिल हैं।
मामलों में अचानक वृद्धि से मची हलचल
पिछले कुछ हफ्तों में चिकनगुनिया के मामलों में तेजी से बढ़ोतरी हुई है। चीन में यह बीमारी पहले कभी इतने बड़े स्तर पर नहीं फैली थी। माना जा रहा है कि यह वायरस विदेशों से यात्रा करके आए लोगों के माध्यम से आया, और अनुकूल पर्यावरण के कारण स्थानीय स्तर पर मच्छरों द्वारा फैलने लगा।
चिकनगुनिया वायरस संक्रमित एडीज मच्छर के काटने से फैलता है। इसके लक्षणों में तेज बुखार, जोड़ों में तेज दर्द, त्वचा पर चकत्ते, थकान और सिरदर्द शामिल हैं। यह बीमारी जानलेवा नहीं होती, लेकिन इससे पीड़ित व्यक्ति लंबे समय तक शारीरिक तकलीफ झेल सकता है, खासकर बुज़ुर्गों और पहले से बीमार लोगों के लिए।
सरकार की सख्त और रचनात्मक कार्यवाही
ड्रोन और जुर्माने के जरिए निगरानी
संक्रमण को रोकने के लिए स्थानीय प्रशासन ने ड्रोन की मदद से मच्छरों के प्रजनन स्थलों की पहचान करना शुरू कर दिया है। ये ड्रोन छतों, निर्माण स्थलों और बाग-बगिचों में जमा हुए पानी को ढूंढते हैं जहाँ मच्छर अंडे देते हैं।
इसके साथ ही, नागरिकों और संस्थानों को अपनी संपत्ति से स्थिर पानी हटाने के आदेश दिए गए हैं। जो लोग इन नियमों का पालन नहीं करते, उन्हें 10,000 युआन तक जुर्माना भरना पड़ सकता है। यह प्रणाली महामारी के समय की निगरानी शैली की याद दिलाती है।
प्राकृतिक तरीकों से मच्छर नियंत्रण
सरकार ने रासायनिक दवाओं पर निर्भरता घटाने के लिए प्राकृतिक उपाय भी अपनाए हैं। जल स्रोतों में मच्छर खाने वाली मछलियाँ डाली गई हैं और ‘हाथी मच्छरों’ को छोड़ा गया है, जो अन्य मच्छरों के लार्वा को खाते हैं लेकिन खुद कोई बीमारी नहीं फैलाते।
अस्पताल में भर्ती और निगरानी
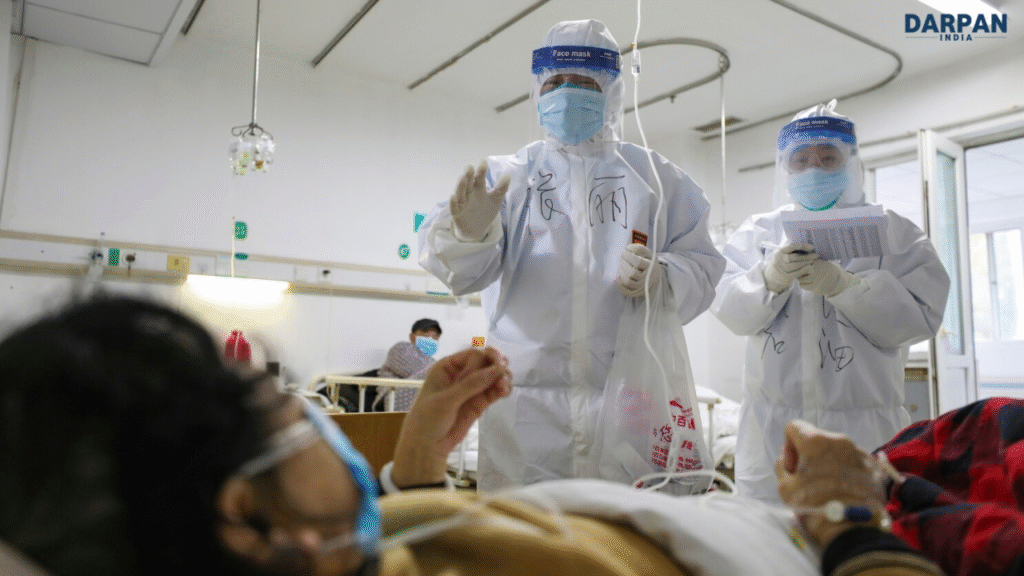
संक्रमित लोगों को स्थानीय अस्पतालों में कम से कम एक सप्ताह के लिए भर्ती किया जा रहा है। हालांकि यह वायरस एक व्यक्ति से दूसरे व्यक्ति को नहीं फैलता, फिर भी मरीजों को निगरानी में रखा जा रहा है। चिकनगुनिया का कोई विशेष इलाज नहीं है, लेकिन लक्षणों को कम करने के लिए आराम, पानी और बुखार कम करने की दवाइयों का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
विशेषज्ञों की राय और चिंता
चिकित्सा विशेषज्ञ इस स्थिति को गंभीर चेतावनी मान रहे हैं। चूंकि चीन में पहले कभी इस बीमारी का इतना व्यापक प्रसार नहीं हुआ था, इसलिए अधिकांश लोग इस वायरस के प्रति प्रतिरक्षा विहीन हैं। इससे वायरस को तेजी से फैलने का अवसर मिल रहा है।
विशेषज्ञों ने जनता को सतर्क रहने, मच्छरों से बचाव के उपाय अपनाने और लक्षण दिखने पर तुरंत डॉक्टर से संपर्क करने की सलाह दी है। साथ ही यह भी कहा गया है कि बीमारी को रोकने के लिए समुदाय स्तर पर स्वच्छता, जल स्रोतों की सफाई और शिक्षा बेहद जरूरी है।
यात्रा चेतावनी और क्षेत्रीय प्रभाव
अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य एजेंसियों ने दक्षिण चीन के लिए यात्रा सलाह जारी की है। यात्रियों को मच्छरों से बचने के लिए पूर्ण आस्तीन वाले कपड़े पहनने, मच्छर भगाने वाली क्रीम का इस्तेमाल करने और मच्छरदानी या वातानुकूलित कमरों में रहने की सलाह दी गई है।
हवाई अड्डों और परिवहन केंद्रों पर यात्रियों को इस बीमारी के बारे में जानकारी दी जा रही है। जैसे-जैसे वैश्विक तापमान बढ़ता जा रहा है और शहरीकरण बढ़ रहा है, वैसे-वैसे इस तरह की बीमारियाँ नए क्षेत्रों में फैलने का खतरा बढ़ गया है।
क्या है चिकनगुनिया वायरस?
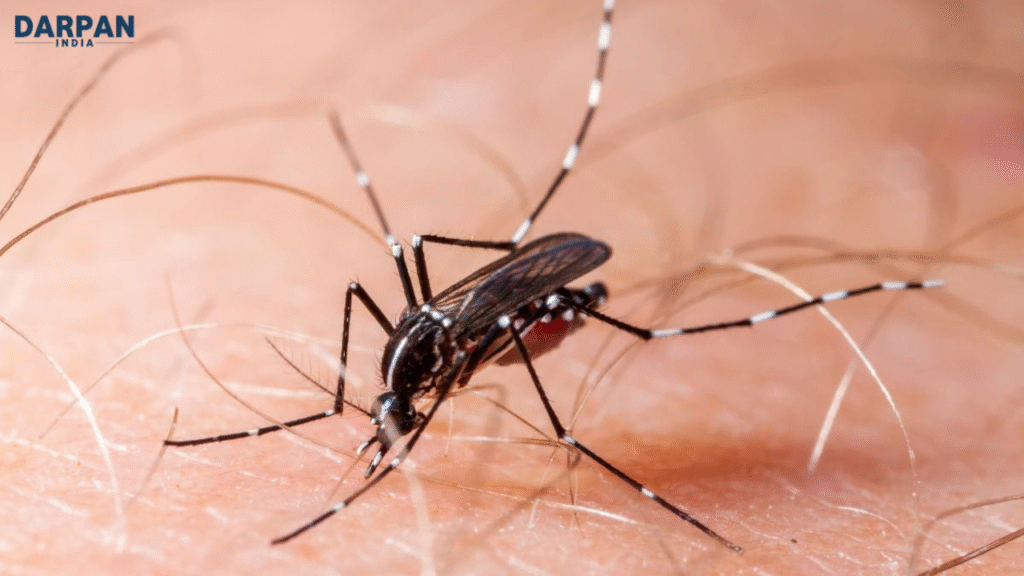

चिकनगुनिया एक वायरल संक्रमण है, जो संक्रमित मच्छर के काटने से होता है। संक्रमण के लक्षण आमतौर पर 2 से 12 दिनों के भीतर प्रकट होते हैं।
मुख्य लक्षण:
- तेज बुखार
- जोड़ों और मांसपेशियों में दर्द
- त्वचा पर चकत्ते
- थकान
- सिरदर्द और मतली
अधिकांश मरीज कुछ ही दिनों में ठीक हो जाते हैं, लेकिन कई मामलों में जोड़ों का दर्द कई हफ्तों तक बना रह सकता है। अभी इस बीमारी का कोई निश्चित इलाज नहीं है। उपचार मुख्य रूप से लक्षणों को कम करने पर केंद्रित होता है।
हाल ही में कुछ देशों में टीके (वैक्सीन) स्वीकृत हुए हैं, लेकिन वे अभी चीन में व्यापक रूप से उपलब्ध नहीं हैं।
इस प्रकोप का महत्व क्यों है
यह प्रकोप सिर्फ एक स्थानीय स्वास्थ्य समस्या नहीं है, बल्कि यह दर्शाता है कि किस तरह संक्रामक बीमारियाँ तेजी से दुनिया भर में फैल सकती हैं। बढ़ता तापमान, शहरीकरण और यात्रा का विस्तार ऐसे वायरस को नए इलाकों में फैलने का अवसर दे रहा है।
इस वायरस का तेजी से फैलना और आम जनसंख्या की रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता का अभाव इसे एक गंभीर सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य चुनौती बना देता है।
चीन की आगे की रणनीति
सरकार ने निगरानी बढ़ाने, सार्वजनिक जागरूकता फैलाने और स्वच्छता अभियानों को तेज़ करने के निर्देश दिए हैं। स्थानीय निकाय लोगों को मच्छरों के प्रजनन स्थल हटाने, जल निकासी की व्यवस्था सुधारने और नियमित सफाई करने के लिए प्रेरित कर रहे हैं।
स्वास्थ्य विभाग भविष्य की बीमारियों के खिलाफ तैयार रहने के लिए नीति स्तर पर सुधार, शोध, और अंतर-संस्था समन्वय की योजना भी बना रहा है।